The Economic Impact of Agriculture and Forest Industries in Virginia
This 2022 study looks at the widespread impact of the forestry and agriculture industries on Virginia’s economy. Relative to the state economy, agriculture industry impacts represent approximately 7.4% of Virginia’s GDP and the forest industry represents 1.9%. However, Virginia agriculture and forest industries affect every other industry in the commonwealth to some degree.
In 2021, the direct impact of Virginia agriculture and forest industries was $55 billion in total output, approximately 185,500 employees, and $23.1 billion in value-added. Agriculture production is the largest component in terms of employment at 28%. The total economic impact (including direct, indirect, and induced impacts) of agriculture and forest industries was nearly $106 billion in total industry output or sales, which is an estimated 11.2% of state output. Every job created in the agriculture and forest industries results in another 1.6 jobs in the Virginia economy and every dollar generated in value-added results in another $1.39 value added in the Virginia economy.
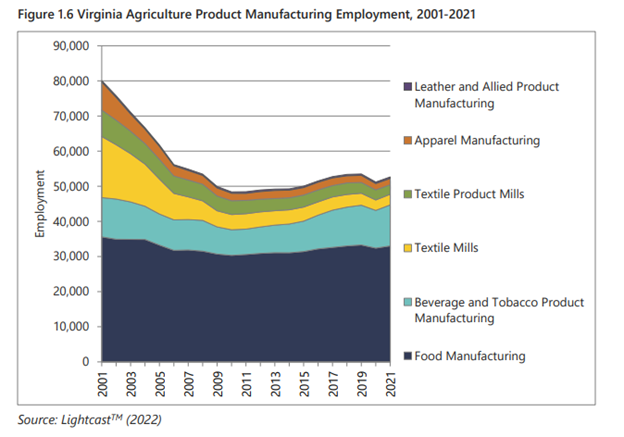
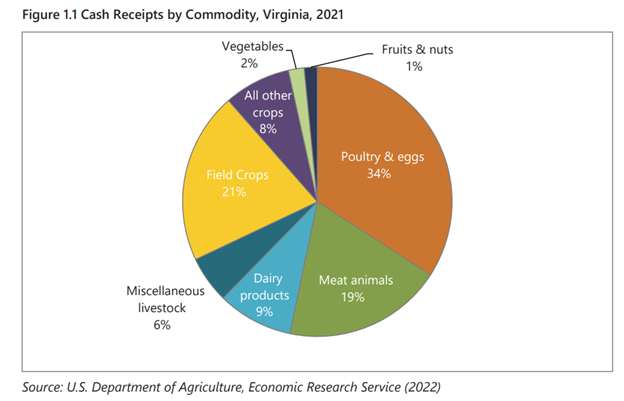
The supply chain disruptions and brief but deep recession following the COVID-19 pandemic had a negative impact on both the forestry and agriculture sectors. Virginia’s agricultural commodity mix has also changed in recent years, seeing cash receipts increase for broilers (meat chickens), corn, soybean, and all other crops (mainly greenhouse and nursery products), and decrease for dairy, cattle, turkey, and tobacco.
The agriculture industry accounts for over 78% of total agriculture and forest industry output and employment impacts, and 79% of value-added impact, with forest industry making up the remainder. The total employment impact of the combined industries rose from 478,079 jobs in 2016 to 490,295 jobs in 2021 (3%) and the total value-added impact grew from $50.1 billion in 2016 to $55.1 billion (10%) expressed in terms of 2021 real dollars.
For the full report, download the file below.